The state of Kotlin for Jakarta EE/MicroProfile traditional applications
22 April 2019

This easter I had the opportunity to catch up with some R&D tasks in my main Job, in short I had to evaluate the feasibility of using Kotlin in regular Jakarta EE/MicroProfile projects including:
- Language benefits
- Jakarta EE/MicroProfile API support, specifically CDI, JPA, JAX-RS
- Maven support
- Compatibility with my regular libraries (Flyway, SL4J, Arquillian)
- Regular application server support -e.g Payara-
- Tooling support (deployment, debugging, project import)
- Cloud deployment by Docker
TL;DR version
Kotlin works as language and plays well with Maven, I'm able to use many of the EE API for "services", however the roadblock is not the language or libraries, is the tooling support.
The experience is superb on IntelliJ IDEA and all works as expected, however the IDE is a barrier if you're not an IntelliJ user, Kotlin doesn't play well with WTP on Eclipse (hence it doesn't deploy to app servers) and Kotlin support for Netbeans is mostly dead.
About language
If you have a couple of years in the JVM space you probably remember that Scala, Ceylon and Kotlin have been considered as better Javas. I do a lot of development in different languages including Java for backends, Kotlin for mobile, JavaScript on front-ends, Bash for almost every automation task so I knew the streghts of Kotlin from the mobile space where is specially important, basically most of the Java development on Android is currently a Java 7+Lambdas experience.
My top five features that could help you in your EE tasks are
* One line functions
* Public by default
* Multiline Strings
* Companion objects
* Type inference
I'll try to exemplify these in a regular application
The Jakarta EE/MicroProfile application
The demo application follows a simple structure, it includes MicroProfile Config, CDI, EJB, JPA, and JAX-RS, focused on a simple phrase collector/retrieval service. Interesting Kotlin features are highlighted.
Source code is available at GitHub repo https://github.com/tuxtor/integrum-ee.
Project configuration
To enable Kotlin support I basically followed Kotlin's Maven guide, is not so explanatory but if you have a litle bit of experience in maven this won't be a problem.
Besides adding Kotlin dependencies to a regular EE pom.xmla special configuration is needed for the all-open plugin, Jakarta EE works with proxy entities that inherit from your original code. To make it simple all CDI, EJB and JAX-RS important annotations were included as "open activators".
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${kotlin.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>compile</id>
<goals> <goal>compile</goal> </goals>
<configuration>
<sourceDirs>
<sourceDir>${project.basedir}/src/main/kotlin</sourceDir>
<sourceDir>${project.basedir}/src/main/java</sourceDir>
</sourceDirs>
</configuration>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>test-compile</id>
<goals> <goal>test-compile</goal> </goals>
<configuration>
<sourceDirs>
<sourceDir>${project.basedir}/src/test/kotlin</sourceDir>
<sourceDir>${project.basedir}/src/test/java</sourceDir>
</sourceDirs>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<compilerPlugins>
<plugin>all-open</plugin>
</compilerPlugins>
<pluginOptions>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.ws.rs.Path</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.enterprise.context.RequestScoped</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.enterprise.context.SessionScoped</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.enterprise.context.ApplicationScoped</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.enterprise.context.Dependent</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.ejb.Singleton</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.ejb.Stateful</option>
<option>all-open:annotation=javax.ejb.Stateless</option>
</pluginOptions>
</configuration>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jetbrains.kotlin</groupId>
<artifactId>kotlin-maven-allopen</artifactId>
<version>${kotlin.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
Model
Table models are easily created by using Kotlin's Data Classes, note the default values on parameters and nullable types for autogenerated values, using an incrementable value on a table.
@Entity
@Table(name = "adm_phrase")
@TableGenerator(name = "admPhraseIdGenerator", table = "adm_sequence_generator", pkColumnName = "id_sequence", valueColumnName = "sequence_value", pkColumnValue = "adm_phrase", allocationSize = 1)
data class AdmPhrase(
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.TABLE, generator = "admPhraseIdGenerator")
@Column(name = "phrase_id")
var phraseId:Long? = null,
var author:String = "",
var phrase:String = ""
)
After that, I need to provide also a repository, the repository is a classic CRUD component injectable with CDI, one line methods are created to make the repository concise. The interesting part however is that Kotlin's nullability system plays well with CDI by using lateinit.
The most pleasant part is to create JPQL querys with multiline declarations, In general I dislike the + signs polluting my query in Java :).
@RequestScoped
class AdmPhraseRepository @Inject constructor() {
@Inject
private lateinit var em:EntityManager
@PostConstruct
fun init() {
println ("Booting repository")
}
fun create(admPhrase:AdmPhrase) = em.persist(admPhrase)
fun update(admPhrase:AdmPhrase) = em.merge(admPhrase)
fun findById(phraseId: Long) = em.find(AdmPhrase::class.java, phraseId)
fun delete(admPhrase: AdmPhrase) = em.remove(admPhrase)
fun listAll(author: String, phrase: String): List<AdmPhrase> {
val query = """SELECT p FROM AdmPhrase p
where p.author LIKE :author
and p.phrase LIKE :phrase
"""
return em.createQuery(query, AdmPhrase::class.java)
.setParameter("author", "%$author%")
.setParameter("phrase", "%$phrase%")
.resultList
}
}
Controller
The model needs to be exposed by using a controller, hence a JAX-RS activator is needed
@ApplicationPath("/rest")
class RestApplication : Application()
That's all the code.
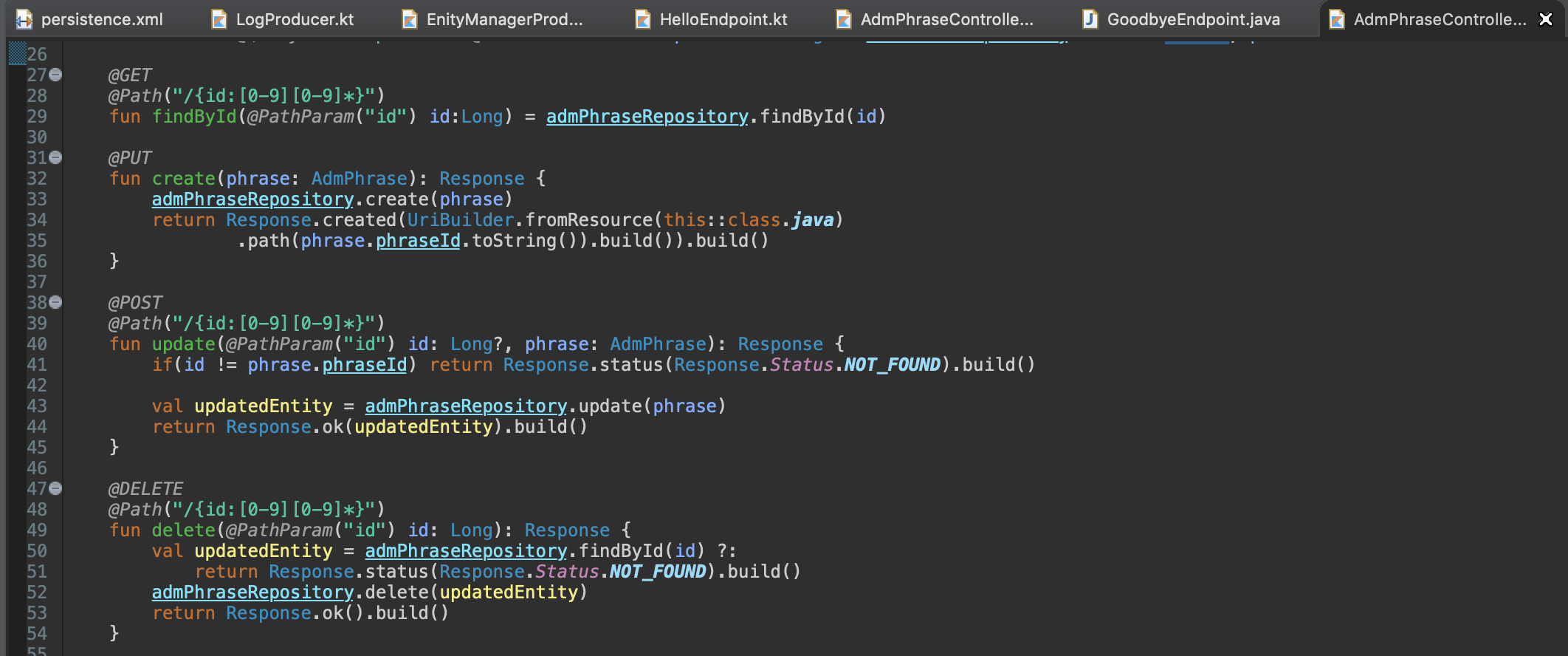
On the other side, implementing the controller looks a lot more like Java, specially if the right HTTP codes are needed. In this line to express the Java class to the builders the special Kotlin syntax this::class.java is mandatory.
Is also observed the elvis operator in action (in DELETE), if the entity is not found the alternative return is fired immediately, a nice idiomatic resource.
@Path("/phrases")
@Produces(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
@Consumes(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
class AdmPhraseController{
@Inject
private lateinit var admPhraseRepository: AdmPhraseRepository
@Inject
private lateinit var logger: Logger
@GET
fun findAll(@QueryParam("author") @DefaultValue("%") author: String,
@QueryParam("phrase") @DefaultValue("%") phrase: String) =
admPhraseRepository.listAll(author, phrase)
@GET
@Path("/{id:[0-9][0-9]*}")
fun findById(@PathParam("id") id:Long) = admPhraseRepository.findById(id)
@PUT
fun create(phrase: AdmPhrase): Response {
admPhraseRepository.create(phrase)
return Response.created(UriBuilder.fromResource(this::class.java)
.path(phrase.phraseId.toString()).build()).build()
}
@POST
@Path("/{id:[0-9][0-9]*}")
fun update(@PathParam("id") id: Long?, phrase: AdmPhrase): Response {
if(id != phrase.phraseId) return Response.status(Response.Status.NOT_FOUND).build()
val updatedEntity = admPhraseRepository.update(phrase)
return Response.ok(updatedEntity).build()
}
@DELETE
@Path("/{id:[0-9][0-9]*}")
fun delete(@PathParam("id") id: Long): Response {
val updatedEntity = admPhraseRepository.findById(id) ?:
return Response.status(Response.Status.NOT_FOUND).build()
admPhraseRepository.delete(updatedEntity)
return Response.ok().build()
}
}
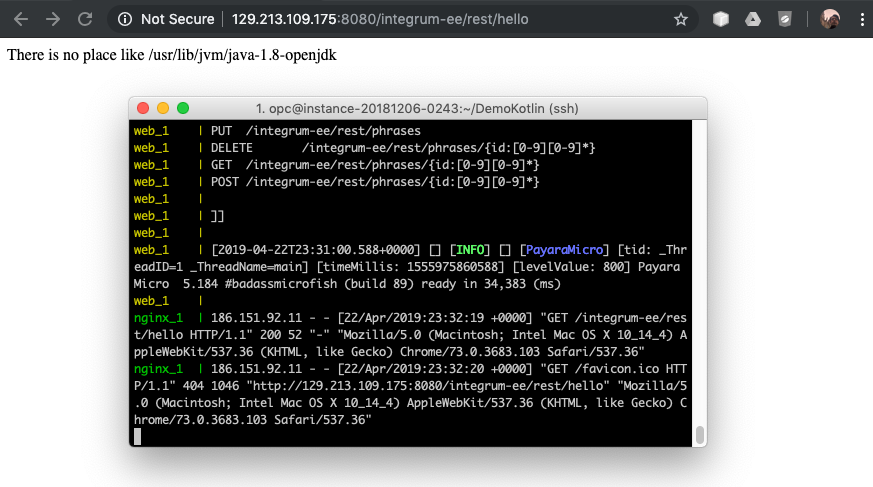
To try MicroProfile a second controller is created that tries to read JAVA_HOME
@Path("/hello")
class HelloController{
@Inject
@ConfigProperty(name ="JAVA_HOME", defaultValue = "JAVA_HOME")
lateinit var javaHome:String
@GET
fun doHello() = "There is no place like $javaHome"
}
Utilities
To create a real test, four "advanced components" were included, being an entity manager producer for CDI components, a Flyway bootstrapper with @Startup EJB, a Log producer for SL4J, and a "simple" test with Arquillian.
The producer itself is pretty similar to its Java equivalent, it only takes advantage of one line methods.
@ApplicationScoped
class EntityManagerProducer {
@PersistenceUnit
private lateinit var entityManagerFactory: EntityManagerFactory
@Produces
@Default
@RequestScoped
fun create(): EntityManager = this.entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager()
fun dispose(@Disposes @Default entityManager: EntityManager) {
if (entityManager.isOpen) {
entityManager.close()
}
}
}
The Flyway migration is implemented with EJB to fire it every time that this application is deployed (and of course to test EJB). Since Kotlin doesn't have a try-with-resources structure the resource management is implemented with a let block, making it really readable. Besides this if there is a problem the data source it will be null and let block won't be executed.
@ApplicationScoped
@Singleton
@Startup
class FlywayBootstrapper{
@Inject
private lateinit var logger:Logger
@Throws(EJBException::class)
@PostConstruct
fun init() {
val ctx = InitialContext()
val dataSource = ctx.lookup("java:app/jdbc/integrumdb") as? DataSource
dataSource.let {
val flywayConfig = Flyway.configure()
.dataSource(it)
.locations("db/postgresql")
val flyway = flywayConfig.load()
val migrationInfo = flyway.info().current()
if (migrationInfo == null) {
logger.info("No existing database at the actual datasource")
}
else {
logger.info("Found a database with the version: ${migrationInfo.version} : ${migrationInfo.description}")
}
flyway.migrate()
logger.info("Successfully migrated to database version: {}", flyway.info().current().version)
it?.connection?.close()
}
ctx.close()
}
}
To create a non empty-database a PostgreSQL migration was created at db/postgresql in project resources.
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.adm_sequence_generator (
id_sequence VARCHAR(75) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL,
sequence_value BIGINT DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT adm_sequence_generator_pk PRIMARY KEY (id_sequence)
);
COMMENT ON COLUMN public.adm_sequence_generator.id_sequence IS 'normal_text - people name, items short name';
COMMENT ON COLUMN public.adm_sequence_generator.sequence_value IS 'integuer_qty - sequences, big integer qty';
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.adm_phrase
(
phrase_id BIGINT DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL,
author varchar(25) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL,
phrase varchar(25) DEFAULT '' NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT adm_phrase_pk PRIMARY KEY (phrase_id)
);
insert into adm_phrase values (1, 'Twitter','Kotlin is cool');
insert into adm_phrase values (2, 'TIOBE','Java is the king');
Log producer also gets benefits from one line methods
open class LogProducer{
@Produces
fun produceLog(injectionPoint: InjectionPoint): Logger =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(injectionPoint.member.declaringClass.name)
}
Finally a test class is also implemented, since Kotlin doesn't have static methods a companion object with @JvmStatic annotation is created on the class, otherwise test won't be executed. This is probably one of the examples where Kotlin's program get bigger if compared to Java equivalent.
@RunWith(Arquillian::class)
class AdmPhraseRepositoryIT {
@Inject
private lateinit var admPhraseRepository: AdmPhraseRepository
companion object ArquillianTester{
@JvmStatic
@Deployment
fun bootstrapTest(): WebArchive {
val war = createBasePersistenceWar()
.addClass(AdmPhraseRepository::class.java)
.addAsWebInfResource("test-beans.xml", "beans.xml")
println(war.toString(true))
return war
}
}
@Test
fun testPersistance(){
val phrase = AdmPhrase( author = "Torvalds", phrase = "Intelligence is the ability to avoid doing work, yet getting the work done")
admPhraseRepository.create(phrase)
assertNotNull(phrase.phraseId)
}
}
Testing the application with IntelliJ IDEA and Payara 5
If the application is executed/debugged on IntelliJ IDEA all works as expected, sincerely I wasn't expecting an easy road but this worked really well. For instance a debugging session is initiated with Payara 5:
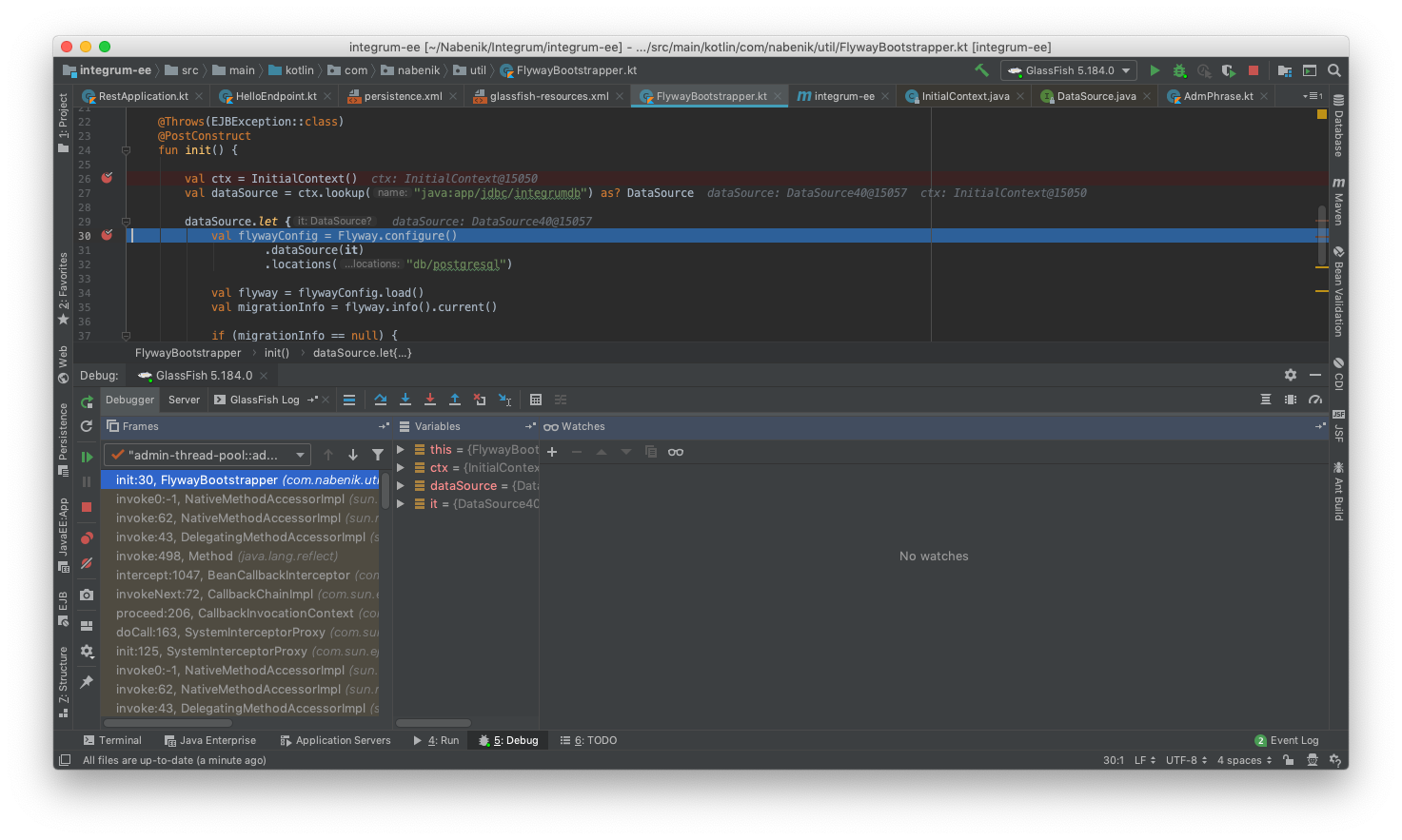
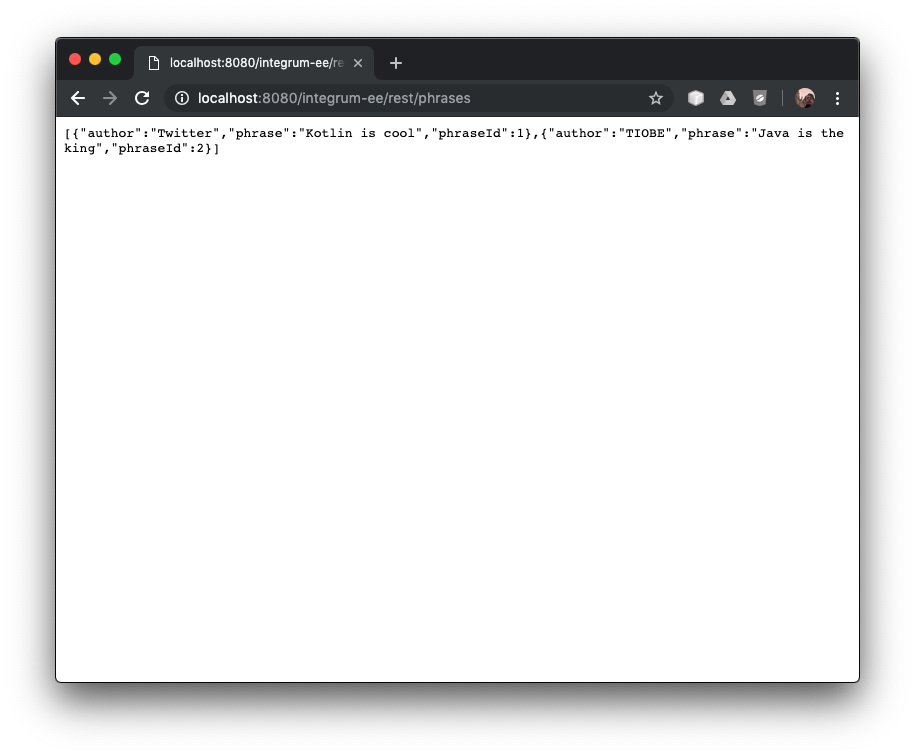
I could also retrieve the results from RDMBS
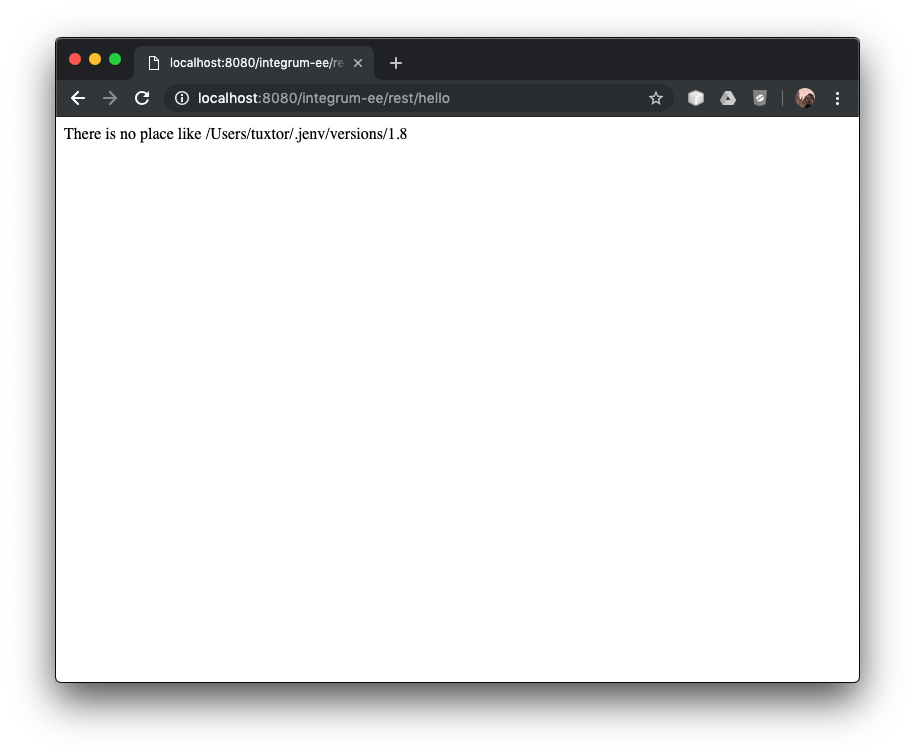
And my hello world with MicroProfile works too
 .
.
Testing the application on Oracle Cloud
As Oracle Groundbreaker Ambassador I have access to instances on Oracle Cloud, hence I created and deployed the same application just to check if there are any other caveats.
Packing applications in Payara Micro is very easy, basically you copy your application to a predefined location:
FROM payara/micro
COPY target/integrum-ee.war $DEPLOY_DIR
A scalable Docker Compose descriptor is needed to provide a simple load balancer and RDBMS, this step is also applicable with Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, Rancher, etc.
version: '3.1'
services:
db:
image: postgres:9.6.1
restart: always
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: informatica
POSTGRES_DB: integrum
networks:
- webnet
web:
image: "integrum-ee:latest"
restart: always
environment:
JDBC_URL: 'jdbc:postgresql://db:5432/integrum'
JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS: '-Xmx64m'
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: informatica
POSTGRES_DB: integrum
ports:
- 8080
networks:
- webnet
nginx:
image: nginx:latest
volumes:
- ./nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf:ro
depends_on:
- web
ports:
- "4000:4000"
networks:
- webnet
networks:
webnet:
A simple nginx.conf file is created just to balance the access to Payara (eventual and scalable) Workers:
user nginx;
events {
worker_connections 1000;
}
http {
server {
listen 4000;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web:8080;
}
}
}
The JTA resource is created via glassfish-resources.xml expressing RDBMS credentials with env variables:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE resources PUBLIC "-//GlassFish.org//DTD GlassFish Application Server 3.1 Resource Definitions//EN" "http://glassfish.org/dtds/glassfish-resources_1_5.dtd">
<resources>
<jdbc-connection-pool name="postgres_appPool" allow-non-component-callers="false" associate-with-thread="false" connection-creation-retry-attempts="0" connection-creation-retry-interval-in-seconds="10" connection-leak-reclaim="false" connection-leak-timeout-in-seconds="0" connection-validation-method="table" datasource-classname="org.postgresql.ds.PGSimpleDataSource" fail-all-connections="false" idle-timeout-in-seconds="300" is-connection-validation-required="false" is-isolation-level-guaranteed="true" lazy-connection-association="false" lazy-connection-enlistment="false" match-connections="false" max-connection-usage-count="0" max-pool-size="200" max-wait-time-in-millis="60000" non-transactional-connections="false" ping="false" pool-resize-quantity="2" pooling="true" res-type="javax.sql.DataSource" statement-cache-size="0" statement-leak-reclaim="false" statement-leak-timeout-in-seconds="0" statement-timeout-in-seconds="-1" steady-pool-size="8" validate-atmost-once-period-in-seconds="0" wrap-jdbc-objects="true">
<property name="URL" value="${ENV=JDBC_URL}"/>
<property name="User" value="postgres"/>
<property name="Password" value="${ENV=POSTGRES_PASSWORD}"/>
<property name="DatabaseName" value="${ENV=POSTGRES_DB}"/>
<property name="driverClass" value="org.postgresql.Driver"/>
</jdbc-connection-pool>
<jdbc-resource enabled="true" jndi-name="java:app/jdbc/integrumdb" object-type="user" pool-name="postgres_appPool"/>
</resources>
After that, Invoking the compose file will bring the application+infrastructure to life. Now it's time to test it on a real cloud. First the image is published to Oracle's Container Registry
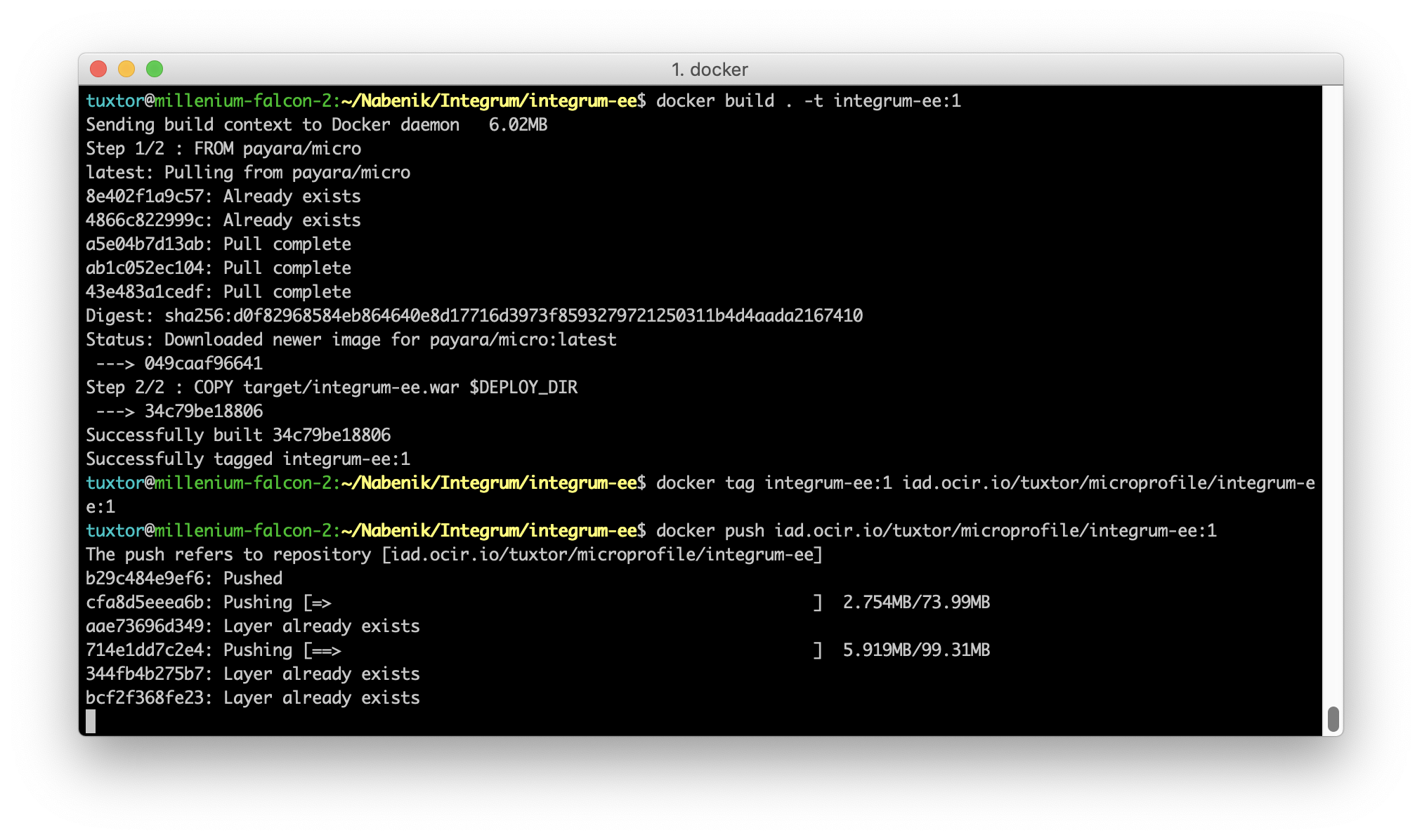
Once the container is available at Oracle Cloud the image become usable for any kind of orchestation, for simplicity I'm running directly the compose file over a bare CentOS VM image (the Wercker+Docker+Kubernetes is an entirely different tutorial).
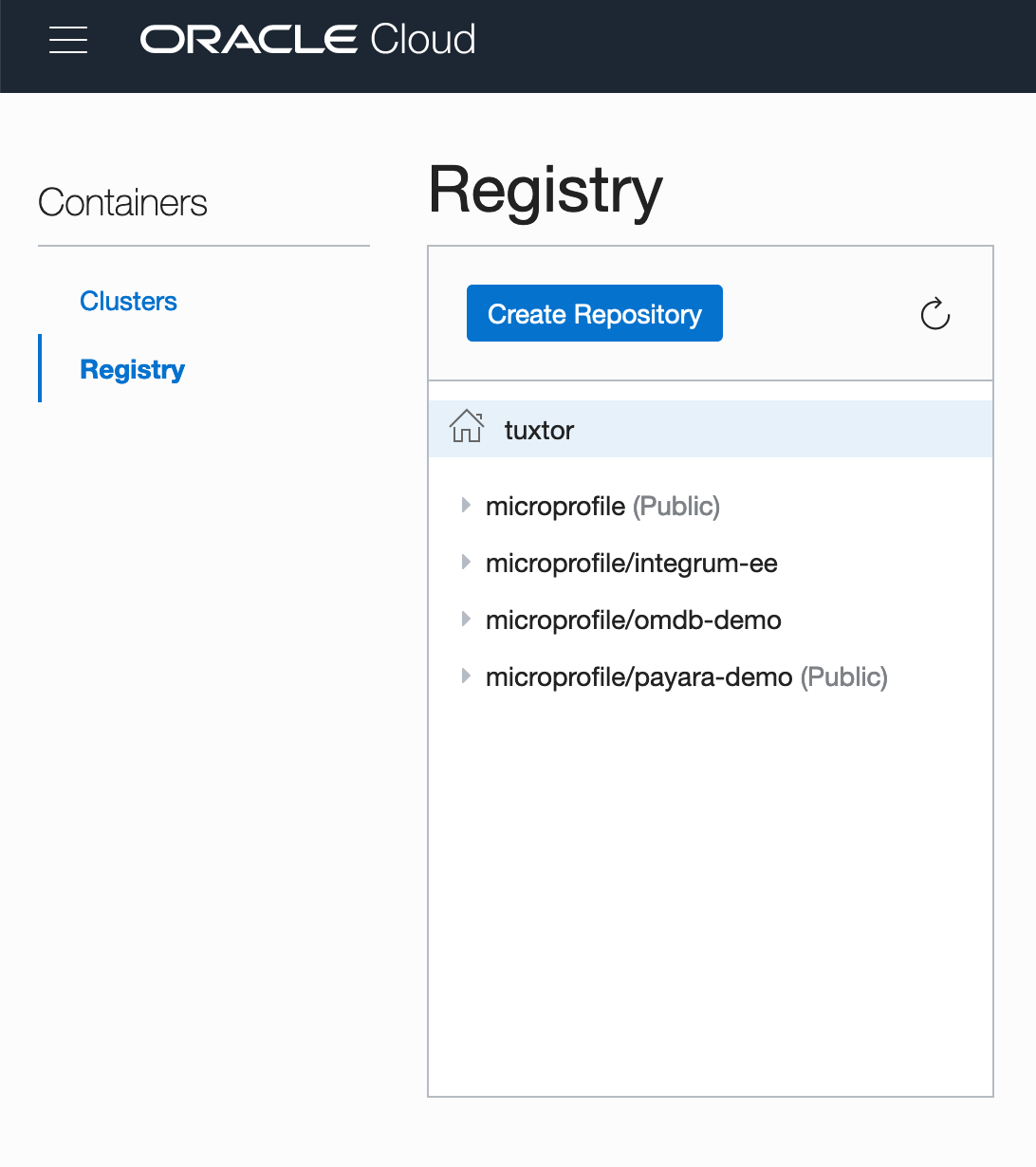
To use it on Oracle's infrasctructure, the image ID should be switched to the full name image: iad.ocir.io/tuxtor/microprofile/integrum-ee:1, in the end the image is pulled, and the final result is our Kotlin EE application running over Oracle Cloud.
Testing the application with NetBeans
JetBrains dropped Kotlin support for NetBeans in 2017, I tried the plugin just for fun on NetBeans 11 but it hangs Netbeans startup while loading Kotlin support, so NetBeans tests were not possible.
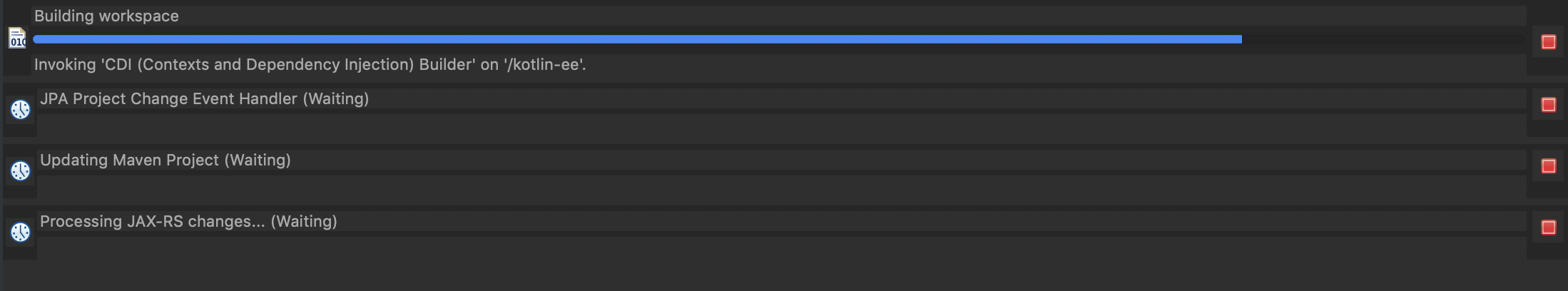
Testing the application with Eclipse for Java EE
JetBeans currently develops a Kotlin complement for Eclipse and seems to work fine with pure Kotlin projects, however the history is very different for Jakarta EE.
After importing the Maven project (previously created in IntelliJ IDEA) many default facets are included in the project, being CDI the most problematic, it takes a lot of time to build the project in the CDI builder step.
Besides that, Jakarta EE complements/parsers work over the code and not the class files, hence the "advanced" menus don't show content, a very cosmetic detail anyway. If Kotlin sources are located under src/main/kotlin as suggested by JetBrains Maven guide, these are ignored by default. Hence, I took the easy road and moved all the code to src/main/java.
Kotlin syntax highlighting works fine, as expected from any language on Eclipse.
However if you try to deploy the application it simply doesn't work because Eclipse compiler does not produce the class file for Kotlin source files, a bug was raised in 2017 and many other users report issues with Tomcat and Wildfly. Basically Eclipse WTP is not compatible with Kotlin and deployment/debugging Kotlin code won't work over an application server.
Final considerations
At the end I was a little dissapointed, Kotlin has great potential for Jakarta EE but it works only if you use IntelliJ IDEA. I'm not sure about IntelliJ CE but as stated in JetBrains website, EE support is only included on Ultimate Edition, maybe this could be changed with more community involvemente but I'm not sure if this is the right direction considering project Amber.

